🌞 What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is a renewable resource derived from the sun’s rays. It’s used for electricity generation, water heating, and various other applications. This guide introduces the core concepts of solar energy and how it powers modern solutions.
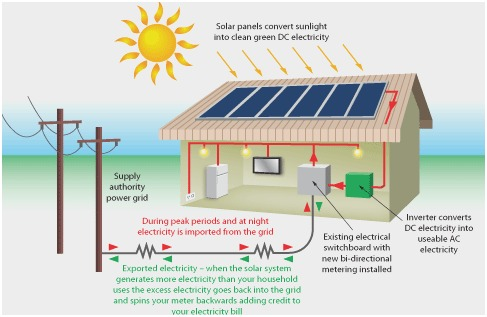
Solar Photovoltaic Systems for Agriculture
Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems are ideal for farms, converting sunlight into electricity through solar cells. This energy can be used to power a wide range of farm activities, from lighting to machinery operation.
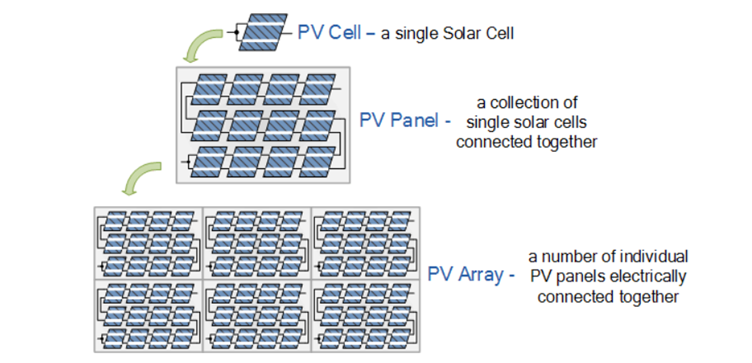
🔋 Solar System Types
Grid-Tied Solar Systems
⚡ Overview: A grid-tied solar system is connected to the national electricity grid. It enables your farm to use solar energy during the day and draw from the grid when necessary, offering seamless energy use.
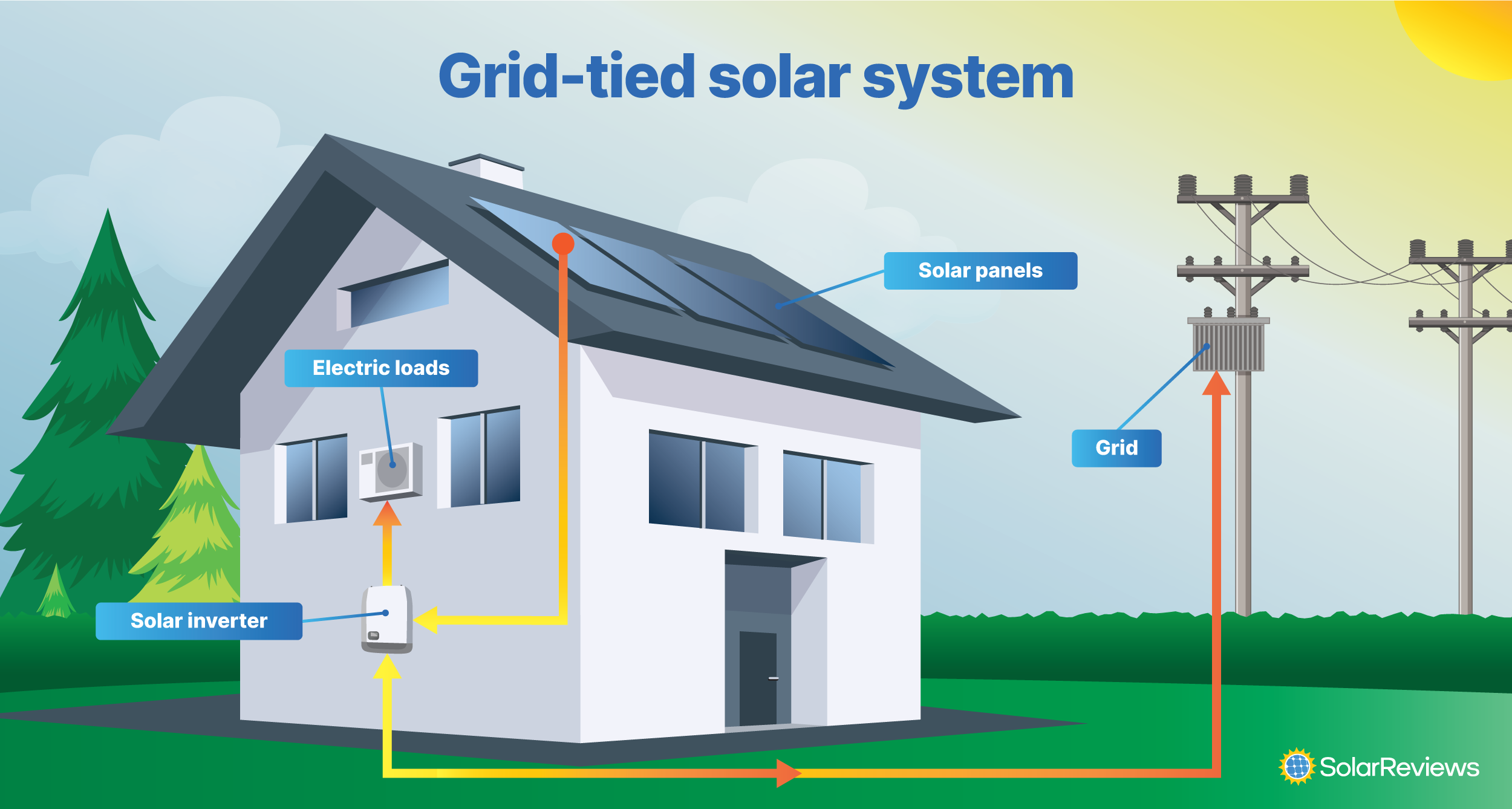
💸 Benefits:
- 💡 Reduced Costs: Solar panels provide power during daylight, lowering electricity bills.
- 🔌 Excess Power: Surplus energy generated by your farm is sent back to the grid, earning you credits or payments through net metering.
- 💰 Lower Initial Investment: Since grid-tied systems don’t require batteries, installation and maintenance costs are lower.
⚙️ Components Needed:
- 🌞 Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it to energy.
- ⚡ Grid-Tie Inverter: Makes the solar energy usable and manages the flow to/from the grid.
- 📊 Power Meter: Measures your farm’s energy use and what is sent back to the grid.
Off-Grid Solar Systems
🌱 Overview: Off-grid systems are self-sufficient and not connected to the electricity grid. They are particularly useful for remote locations or farms with unreliable access to grid power.
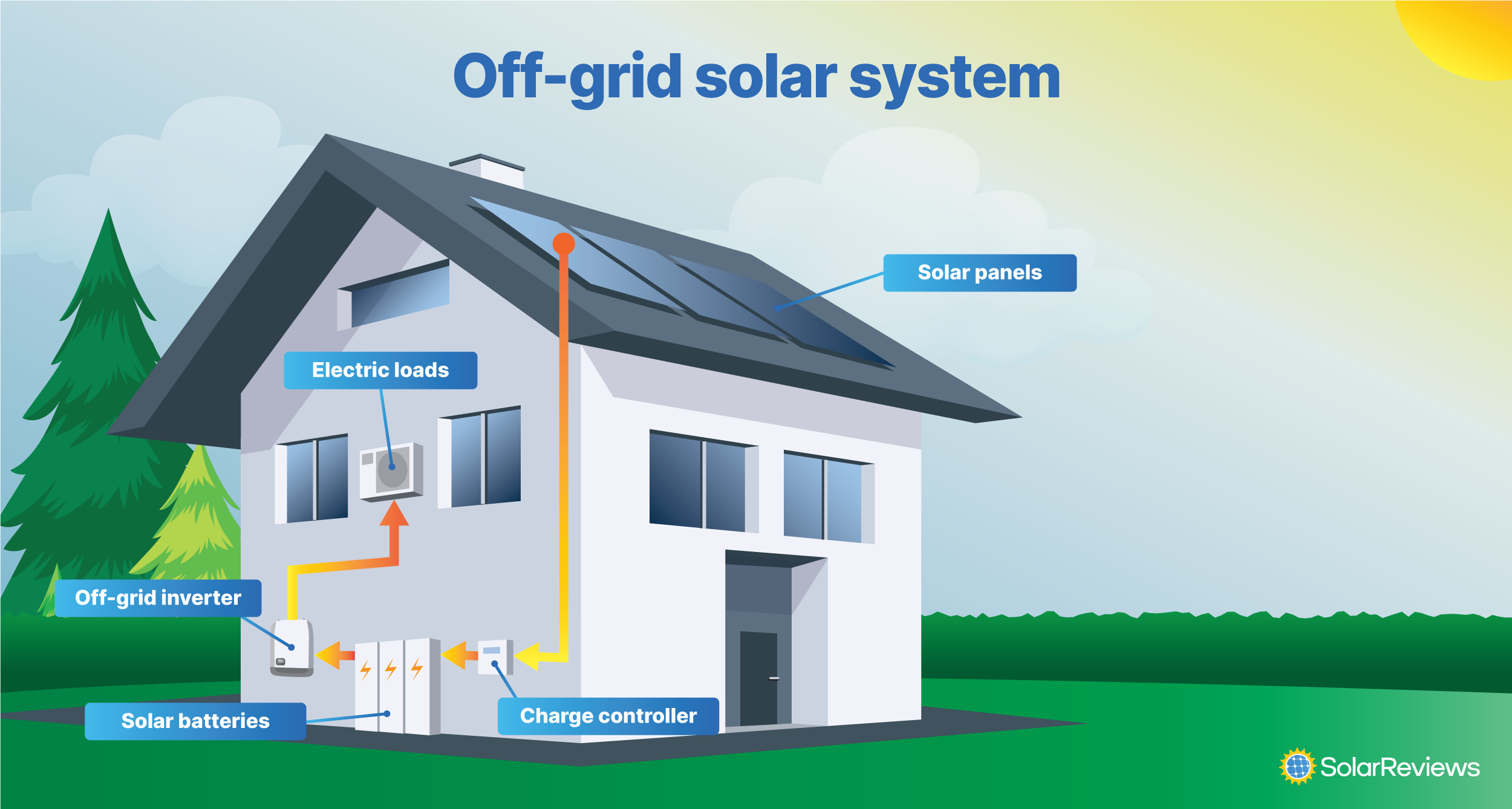
💸 Benefits:
- 🌞 Total Energy Independence: Off-grid systems ensure a steady power supply even in remote areas.
- 💰 Reduced Grid Dependence: Say goodbye to monthly electricity bills by relying on solar power alone.
- 🏞️ Perfect for Remote Locations: Ideal for farms located far from grid infrastructure.
⚙️ Key Components:
- 🌞 Solar Panels: Capture sunlight for energy conversion.
- 🔋 Charge Controller: Regulates the battery’s charging process.
- 🔋 Battery Bank: Stores solar energy for use during nighttime or cloudy periods.
- 🌟 Off-Grid Inverter: Converts stored energy into usable electricity for farm operations.
- ⛽ Backup Generator (Optional): Provides additional power during prolonged cloudy periods.
Hybrid Solar Systems
🔄 Overview: Hybrid systems combine the advantages of both grid-tied and off-grid configurations. They allow the use of solar power, store excess energy in batteries, and only rely on the grid when required, offering a versatile and efficient energy solution.
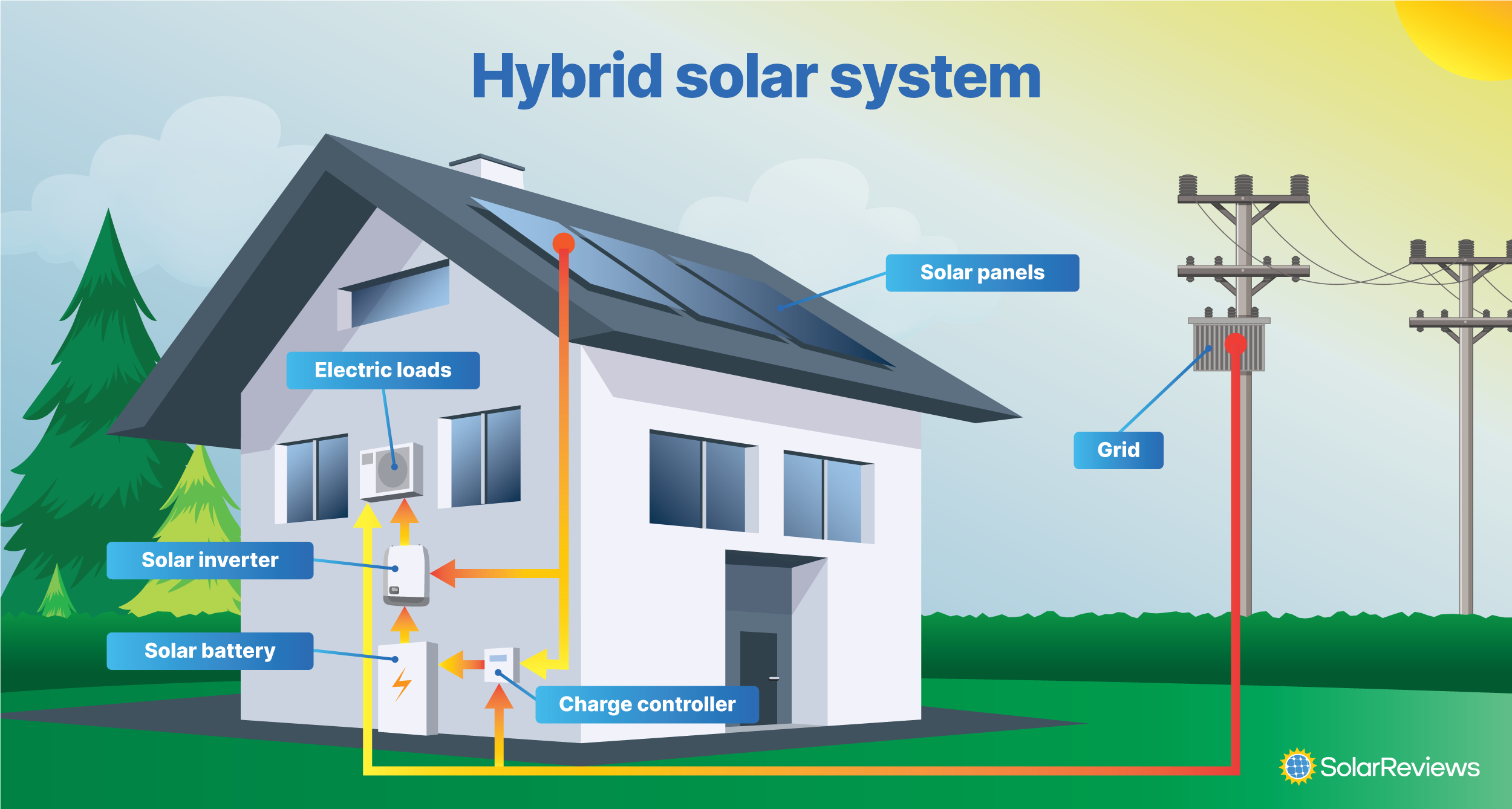
- 🔌 Versatile Power Options: Utilize solar first, store surplus energy, and only tap into the grid when necessary.
- 💸 Cost-Effective: More affordable than fully off-grid systems while offering a reliable power supply without needing a generator.
- ⚙️ Smart Power Management: Optimizes the use of solar, battery, and grid electricity for maximum efficiency.
⚙️ Essential Components:
- 🌞 Solar Panels: Capture solar energy for conversion.
- 🔋 Battery Bank: Stores surplus energy for later use.
- ⚡ Battery-Based Inverter: Controls energy flow between solar panels, batteries, and the grid.
- 📊 Power Meter: Tracks energy usage and credits from the grid.
🛠️ Why Solar Power is Ideal for Farms
- 🌞 Renewable and Reliable: Solar power is sustainable, using the sun’s rays, which are an endless and reliable energy source.
- 💰 Lower Energy Expenses: Solar systems, especially grid-tied ones, can greatly reduce or eliminate electricity bills.
- 🏡 Ideal for Off-Grid Locations: If your farm is remote, solar offers a self-sufficient and cost-effective energy solution without relying on expensive power lines.
- 📈 Increases Property Value: Solar installations can boost the value of your farm, as properties with solar systems tend to sell at higher prices.

